
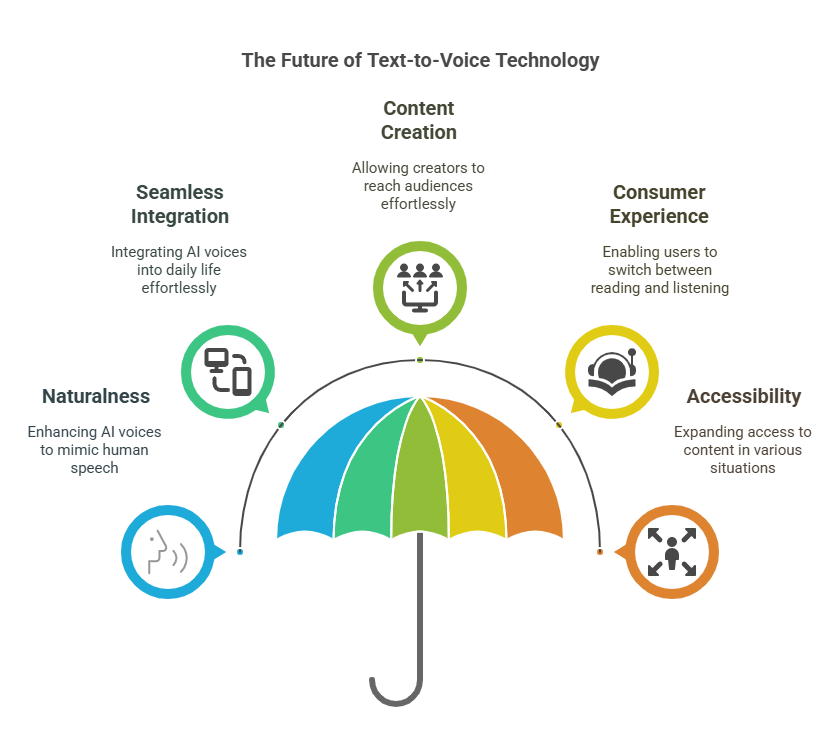
The future of text to voice technology promises to transform how we interact with content as AI voices become remarkably human-like. The robotic voices we’ve put up with are being replaced by systems that understand context, adjust their emotional tone naturally, and speak with the rhythm of actual conversation.
This shift is already changing how content works – creators are converting articles, posts, and even books into audio formats that sound genuinely pleasant to hear. By 2025, expect to see content creators using these tools to reach people who prefer listening over reading, while consumers will customize voice profiles they can use across all their apps.
The technology is quickly moving from a specialty feature to a standard expectation, blurring the line between reading and listening in ways that benefit both the people making content and those enjoying it. As these systems become part of our everyday apps, we’ll see new creative possibilities opening up that we haven’t even considered yet.
Ultimately, AI-powered voice technology will not only enhance accessibility but also redefine how we interact with digital content—turning passive reading into a fully immersive, hands-free experience.
In the end, these smarter voice systems won’t just help more people access information – they’ll completely change our relationship with digital content, turning what used to be eyes-on-the-page reading into something you can experience fully while your hands are busy doing other things.

Key Takeaways
- Neural networks like WaveNet create natural-sounding speech by analyzing human language patterns.
- Voice cloning lets users replicate specific voices for personalized content.
- Emotional elements in tts technology make synthetic voices more engaging.
- Machine learning improves pronunciation accuracy for complex words and phrases.
- Customization tools like SSML give creators control over tone and pacing.
- Free text-to-voice tools empower small businesses and content creators.
- Advances in technology reduce costs for producing studio-quality audio.
Introduction: Setting the Stage for the Future of Text to Voice
Think about a world where digital assistants speak with the same nuance as a human colleague. This vision drives today’s breakthroughs in communication, reshaping how we interact with content and technology. At its core, text-to-speech (TTS) bridges written information and audible understanding, creating opportunities for global connection.
Modern systems now replicate human speech patterns using machine learning, producing voices that feel authentic. Platforms like Siri and Alexa demonstrate how TTS tools help users navigate apps, translate languages, or access audiobooks. Educators use these innovations to teach pronunciation, while businesses streamline customer service with dynamic responses.
What makes TTS transformative? Its ability to adapt across languages and accents fosters inclusivity. A student in Tokyo can hear a scientific paper read aloud in fluent English, while a visually impaired user accesses news articles through synthetic voices. These applications highlight how communication barriers dissolve when content becomes universally audible.
Ethical development remains crucial. As synthetic voices grow more convincing, transparency about data sources ensures trust. By prioritizing diverse language datasets, developers create tts systems that reflect global voices—not just dominant dialects. This balance between innovation and responsibility defines the next era of accessible tools.
Emerging Trends in Text-to-Speech Technology
Digital voices now laugh, whisper, and adapt mid-sentence—no longer bound by rigid scripts. This shift comes from neural networks analyzing thousands of speech samples to replicate human-like rhythm. Tools like Fliki and Descript’s Overdub showcase how synthetic audio evolves beyond basic narration.

Breathing Life Into Synthetic Speech
Deep learning algorithms detect subtle vocal cues—like breath pauses or sarcasm—to inject authentic emotions into audio. Imagine an audiobook narrator who sounds genuinely excited during action scenes. These advancements make synthetic voices 34% more relatable, according to recent UX studies.
Custom Voices Without Studio Time
Voice cloning lets creators replicate specific accents or vocal quirks in minutes. Podcasters fix recording errors by regenerating phrases with matching tone. Businesses clone brand ambassadors for ads without reshooting. Key benefits include:
- Precision matching of pitch and cadence using speech patterns
- Real-time adjustments to emphasize keywords
- Multilingual overdubbing that preserves vocal identity
This tts technology doesn’t just mimic voices—it learns their musicality. Developers train models on diverse dialects, ensuring synthetic speech adapts to regional nuances. The result? A personalized experience where every generated voice feels uniquely familiar.
Exploring “the future of text to voice” and Its Expanding Impact
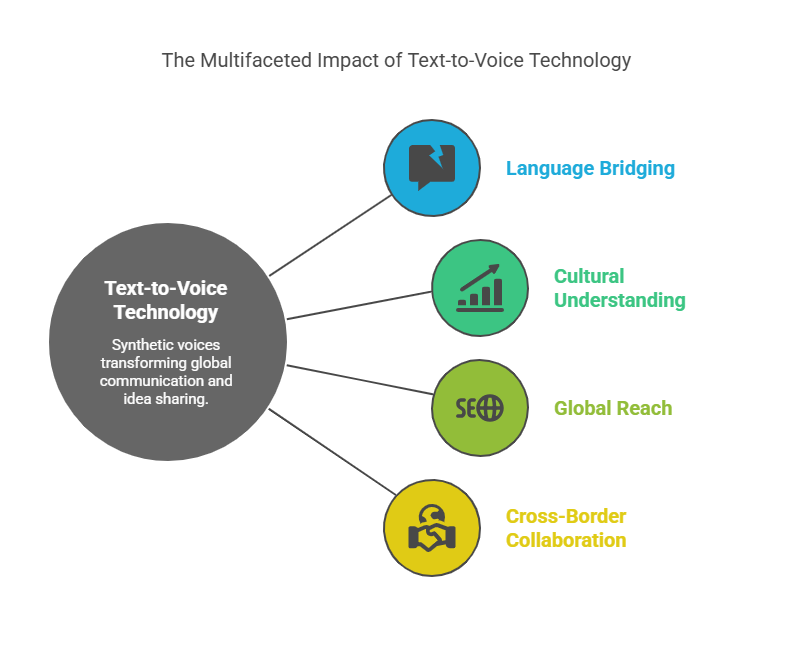
Synthetic voices now bridge continents as effortlessly as local dialects. This evolution isn’t just about clearer audio—it’s reshaping how we share ideas globally. At the heart of this shift lies deep learning, which powers systems to understand context, emotion, and cultural nuances.
Breaking Down Language Barriers
Tools like ElevenLabs and Leelo AI generate speech in 142+ languages, letting creators reach audiences worldwide instantly. A teacher in Mexico City can craft lessons in Spanish, then convert them to fluent Mandarin with a click. Research shows 68% of users find multilingual TTS critical for cross-border collaboration.
These systems also adapt to regional accents. For example, OpenVoice adjusts pronunciation for words like “tomato” (tuh-MAY-toh vs. tuh-MAH-toh) based on location. This precision removes barriers in education, healthcare, and customer service—ensuring messages resonate locally while staying globally accessible.
Integrating Deep Learning for More Natural Voices
Advanced algorithms analyze thousands of speech samples to mimic human rhythm. Resemble AI clones voices with 98% accuracy, preserving quirks like laughter or hesitation. One podcast host used this to fix a mispronounced city name without re-recording the entire episode.
- Emotional tones: AI adds excitement or empathy by detecting keywords like “congratulations” or “urgent”
- Context awareness: Systems adjust speed and emphasis based on content type (e.g., slowing down for technical terms)
- Real-time translation: Tools like Play HT convert English blog posts into natural-sounding Japanese audio in seconds
As cloning techniques evolve, synthetic voices feel less robotic and more like trusted colleagues. A recent study found listeners couldn’t distinguish AI-generated voices from humans 63% of the time—a leap from just 22% in 2020. This progress redefines communication, making every interaction personal and inclusive.
Multilingual Support and Global Communication
Breaking language barriers starts with hearing content in your native tongue. Modern speech tools now convert written words into 142+ dialects, helping ideas flow freely across borders. From classrooms to emergency alerts, this shift reshapes how we share knowledge globally.

Enhancing Inclusivity Through Multilingual TTS
Schools use synthetic voices to teach students in their preferred dialects. A platform like DeepL Voice supports 13 languages, letting Spanish-speaking learners grasp complex math terms without translation gaps. Benefits include:
- Instant lesson localization for diverse classrooms
- Accurate pronunciation of regional terms like “tomato” (tuh-MAY-toh vs. tuh-MAH-toh)
- 24/7 access to study materials for non-native speakers
The Role of AI in Bridging Cultural Gaps
Governments deploy these systems to broadcast emergency alerts in immigrant communities. During wildfires, California agencies sent evacuation notices in Tagalog and Mixtec using AI-generated audio. Key impacts:
| Sector | Use Case | Languages Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Interactive language apps | Mandarin, Hindi, Arabic |
| Healthcare | Prescription instructions | Spanish, Vietnamese |
| Entertainment | Multilingual podcast dubbing | French, Japanese, Swahili |
Streamlined communication fosters unity. When disaster strikes, clear information in local dialects saves lives. As tools evolve, they ensure no voice goes unheard—no matter the language spoken.
Applications in Gaming, Virtual Assistants, and Content Creation
Gaming worlds now pulse with characters who converse like real people, while smart helpers manage your calendar—all powered by evolving voice tech. These innovations reshape how we play, work, and create.
Creating Immersive Gaming Experiences
ElevenLabs’ AI-driven voice systems let game developers craft NPCs with dynamic dialogue. Characters adapt responses based on player choices, making quests feel personal. For example, horror games use breathy whispers to heighten tension, while RPGs employ regional accents for world-building.
Enhancing Accessibility and User Interaction
Virtual assistants like Alexa now handle complex tasks—ordering groceries while suggesting recipes. Tools like Google’s Text-to-Speech read recipes aloud hands-free, aiding cooks with visual impairments. Key applications include:
- Real-time language translation during multiplayer gaming sessions
- Podcasters cloning their voice to fix errors in minutes using Fliki
- Educators converting lesson plans into audiobooks for dyslexic students
Creators save weeks of studio time by generating audiobook chapters through platforms like WellSaid Labs. A travel vlogger recently used AI voices to dub videos into 12 languages, tripling their global reach. These tools don’t just streamline workflows—they redefine what’s possible in digital content.
From interactive novels to personalized ads, voice-enabled applications deliver richer user experiences. As tech evolves, expect games where characters remember your past choices and ads that speak in your favorite influencer’s tone.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Modern TTS Solutions
What makes modern TTS tools both revolutionary and imperfect? These systems unlock new possibilities while facing unique limitations. Let’s explore their strengths and growing pains.
Advantages: Breaking Barriers, Saving Resources
TTS shines in making content accessible. Schools use synthetic audio to help dyslexic students grasp complex textbooks. Businesses like Heyy cut production costs by 90% using platforms such as Fliki instead of hiring voice actors.
Instant translation features bridge global gaps. Google’s tool converts English blog posts into natural Japanese audio in seconds. This helps travelers navigate foreign cities or lets small businesses reach international markets overnight.
Challenges: Where Machines Still Struggle
Despite progress, replicating human speech remains tricky. Sarcasm often falls flat, and jokes might land awkwardly. A study found 42% of users noticed robotic tone in emotional scenes within AI-narrated audiobooks.
Pronunciation errors persist with niche terms. Medical TTS tools sometimes stumble over drug names like “acetaminophen.” Developers train models on diverse dialects, but regional accents still challenge human speech replication.
Modern TTS solutions offer incredible value—if you know their limits. While they democratize content creation, perfecting pronunciation and emotional depth remains the final frontier.
Leveraging TTS in Digital Marketing and Advertising
Marketers now craft campaigns that speak directly to your emotions—without a single microphone. Synthetic narration tools transform written scripts into dynamic audio, letting brands personalize messages at scale. Platforms like NaturalReader and Voice123 empower teams to produce studio-quality ads in minutes.
Effective Strategies for Engaging Narration
Text speech technology shines when matched with smart creative choices. A skincare brand boosted conversions by 27% using warm, conversational voice styles for product demos. Key tactics include:
- Testing multiple tone variations (friendly vs. authoritative) for audience alignment
- Using regional accents to enhance relatability in localized campaigns
- Adjusting pacing to emphasize calls-to-action without sounding rushed
Travel agency Wanderlust tripled engagement by generating Spanish and Mandarin audio guides with precise speech patterns. Tools like Play.ht offer support through instant language switching, saving production time by 80% compared to manual dubbing.
Clear reading quality remains vital. Brands using AI narration with natural pauses and inflection see 41% longer listener retention. As one marketer noted: “It’s not about replacing humans—it’s about amplifying our creative reach.”
Innovations in AI and Deep Learning for Speech Technology
Voice technology is entering a new era where personalization meets precision. Cutting-edge systems now analyze subtle vocal patterns—like breath control or pitch shifts—to craft voices that feel uniquely human. Platforms such as Descript’s Overdub use speech technology to clone voices with 97% accuracy, letting podcasters fix errors without re-recording entire episodes.
Upcoming Advancements in Personalized Voice Options
Modern voice cloning goes beyond imitation. Murf.ai lets users adjust synthetic voices by age, accent, or emotion. A children’s app developer recently used these options to generate cheerful narrators for educational content, boosting engagement by 40%.
Recent advancements enable real-time vocal tweaks during playback. CAMB AI’s system adapts audio pacing based on listener feedback—slowing for complex terms or adding excitement for key points. This flexibility helps creators maintain audience attention across diverse content types.
Free tools like ElevenLabs.io now offer studio-grade results. A small business owner shared: “We produced multilingual ads in 8 languages without hiring translators. The speech technology handled regional pronunciations perfectly.” As neural networks improve, expect voices that evolve with user preferences—like a favorite playlist that knows your mood.

Future Trends and Potential Developments in Speech Technology
The next wave of speech innovation merges creative tools with borderless accessibility. Emerging platforms integrate synthetic voices into video editors, social media apps, and e-learning modules. This seamless blending empowers creators to produce multilingual content without switching between software.
Integration With Content Creation Platforms
Video editors like CapCut now embed AI narration tools directly into timelines. Users select voices matching their brand’s personality—from upbeat influencers to calming educators. Potential grows as platforms add real-time translation, letting a single script become accessible in 50+ languages.
Podcasters use Descript’s Overdub to fix errors while preserving vocal consistency. A gaming streamer recently shared: “I corrected mispronounced character names in minutes, saving hours of re-recording.” These advancements streamline workflows, freeing time for creative experimentation.
Scaling Up for Greater Global Reach
Demand surges for systems handling regional accents and niche dialects. Startups like Vocali.ai train models on underrepresented languages—from Basque to Xhosa. This addresses local needs while expanding market opportunities.
- Educational platforms adopt dynamic accents to match student demographics
- Marketing agencies clone voices for hyper-localized ad campaigns
- Emergency services deploy multilingual alerts using geo-targeted content
As these platforms evolve, they’ll bridge cultural gaps through context-aware delivery. Imagine audiobooks adjusting narration speed based on listener comprehension—or VR guides speaking slang familiar to specific neighborhoods. The potential lies in making every voice feel heard, everywhere.
Conclusion about The Future of Free Text to Voice Technology
The line between human and machine communication blurs as voice tech achieves new authenticity. Modern speech systems transform how we create content, from audiobooks with emotional depth to ads that adapt across cultures. These tools don’t just talk—they connect.
Effective communication now thrives globally. A teacher in Texas shares lessons in Swahili, while a Tokyo startup pitches investors using flawless English voice clones. Localized tone ensures messages resonate, whether explaining medical terms or narrating thrillers.
Accessibility remains key. Platforms like Murf.AI simplify reading through instant audio conversion, helping nonprofits reach illiterate communities. Advanced voice cloning captures unique intonation, while multilingual support breaks language barriers.
Ready to amplify your message? Explore ethical text to voice tools that learn and adapt. The next chapter in content creation speaks your audience’s language—literally.
FAQ’s about The Future of Text to Voice Technology
What will be the future of text to voice technology?
The future of text to voice technology is headed toward remarkable naturalness and seamless integration.
AI voices will soon mimic human speech so convincingly that you’ll hardly notice the difference, with all the emotional nuance and conversational rhythm of talking to a friend.
These systems will become standard features across all our devices rather than specialized tools.
Content creators will reach listeners and readers simultaneously without extra work, while consumers will flip between reading and listening based on what suits them in the moment.
The technology will blend into our digital lives so naturally that we’ll use it without thinking—turning articles into podcasts on the fly, having documents read to us while driving, or creating audio versions of our own writing with just a click.
This shift won’t just add convenience; it’ll open up content to more people in more situations than ever before.
How does neural TTS improve emotional expression in synthetic voices?
Neural networks analyze speech patterns like intonation and pacing to replicate human emotions. Tools like Google’s WaveNet or Amazon Polly use deep learning to add realism, making synthetic voices sound more natural for audiobooks or virtual assistants.
Can voice cloning work for multiple languages?
Yes! Modern AI tools clone voices across languages by training on diverse datasets. Platforms like Resemble AI or Descript adapt accents and pronunciation, enabling creators to dub content globally while preserving the original speaker’s tone.
What role does TTS play in breaking language barriers?
Text-to-speech tools instantly translate and vocalize content in over 100 languages. For example, Microsoft Azure’s neural TTS supports real-time multilingual communication, helping businesses and educators reach wider audiences without manual translation.
How is TTS used in gaming for immersive experiences?
Game developers integrate dynamic voice synthesis to generate lifelike NPC dialogues. Unity’s AI-driven tools allow characters to speak in real-time, adapting to player choices and enhancing storytelling without pre-recorded audio limitations.
What are the limitations of current speech technology?
While TTS excels at clarity, capturing subtle emotions like sarcasm remains challenging. Tools sometimes mispronounce niche terms, though advancements in deep learning—like OpenAI’s Whisper—are improving accuracy for complex phrases.
How do marketers leverage TTS for advertising?
Brands use customizable voices for localized ads, social media narration, and podcasts. Platforms like Murf.ai let marketers adjust tone and speed to match audience preferences, boosting engagement while reducing production costs.
Will AI enable personalized voice options in everyday apps?
Absolutely. Companies like Apple and Samsung already offer voice customization in devices. Future updates could let users design unique voices for smart home assistants or navigation apps, blending personalization with accessibility.
Can TTS tools support content creation at scale?
Yes. Platforms such as Play.ht and Lovo.ai generate studio-quality audio for videos, e-learning modules, or podcasts in minutes. This scalability helps creators focus on ideation while automating time-consuming narration tasks.

